Jube is an open source AML software and open source fraud detection software platform for real-time detection of suspicious transactions, AML case management, and fraud prevention.
Jube is fully open-source (AGPLv3) with all features available and no vendor lock-in, Jube is transparent, auditable, and extensible—keeping your data under your control while enabling rapid adaptation to new products, workflows, regulations, or payment schemes.
See Jube open source AML software and open source fraud detection software in action:
Jube combines real-time transaction monitoring, adaptive machine learning, rule-based detection, and workflow-driven case management into a single, scalable system.
Designed for compliance teams, financial institutions, and fintechs, Jube provides:
- Accurate and interpretable risk scoring using supervised and unsupervised machine learning models
- Rule-based detection with thresholds, velocity checks, aggregation counts, and sanctions screening
- Workflow-driven AML and fraud case management with automated escalation and full audit trails
- Cloud-native deployment with Docker and Kubernetes support, multi-tenancy, configuration preservation, and high-performance caching for low-latency decisioning
Jube ensures accuracy, transparency, and auditability, making it ideal for organizations that must meet strict regulatory requirements while monitoring large transaction volumes.
Key Features
- Trusted open source AML and fraud detection software for compliance and fraud prevention
- Real-time transaction monitoring
- Hybrid detection engine: combining rule‑based logic for open source AML and fraud detection
- Adaptive machine learning models for AML and fraud risk scoring
- Workflow-driven AML and fraud case management
- Fully open source AML and fraud detection software under AGPLv3
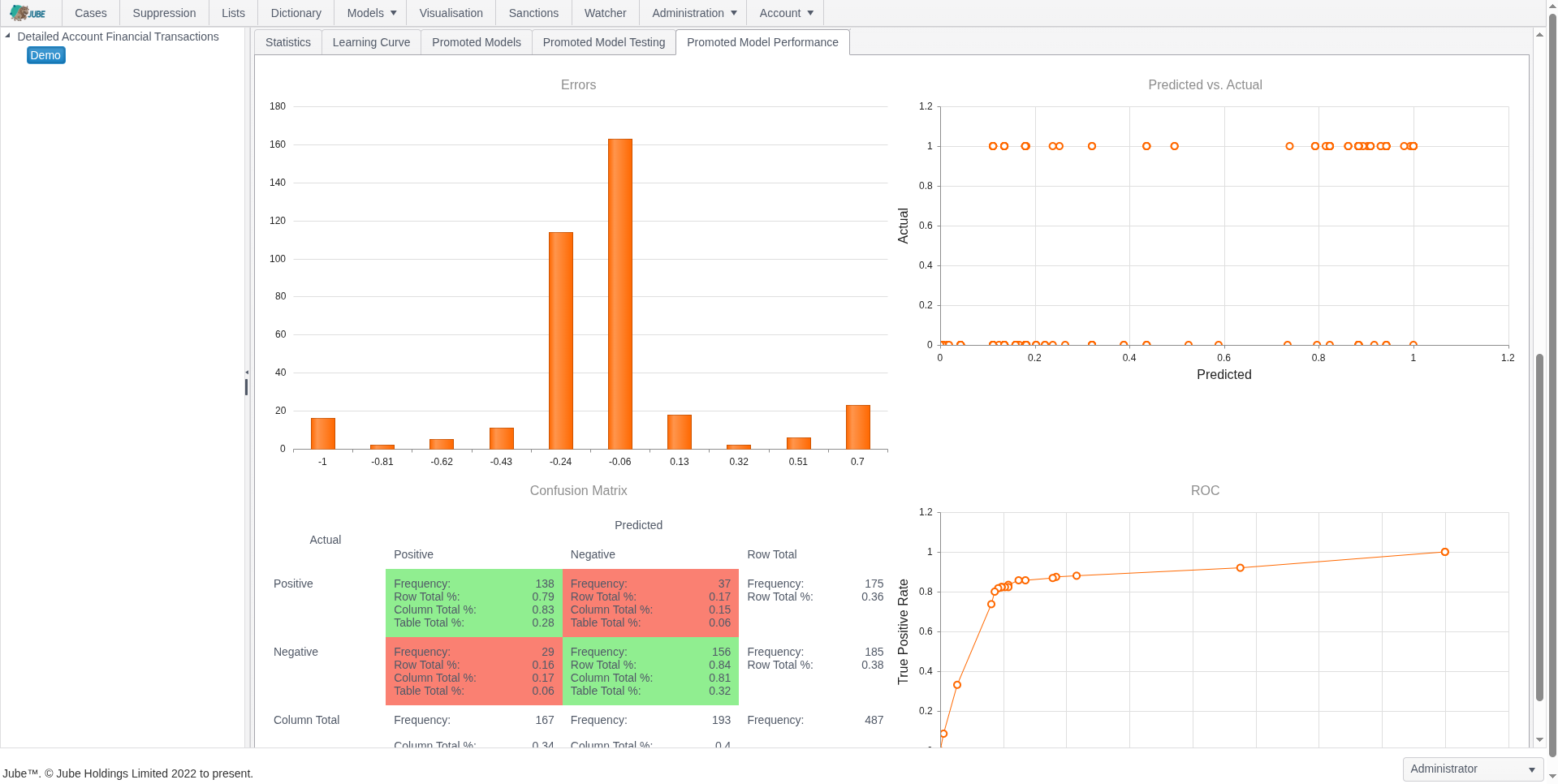
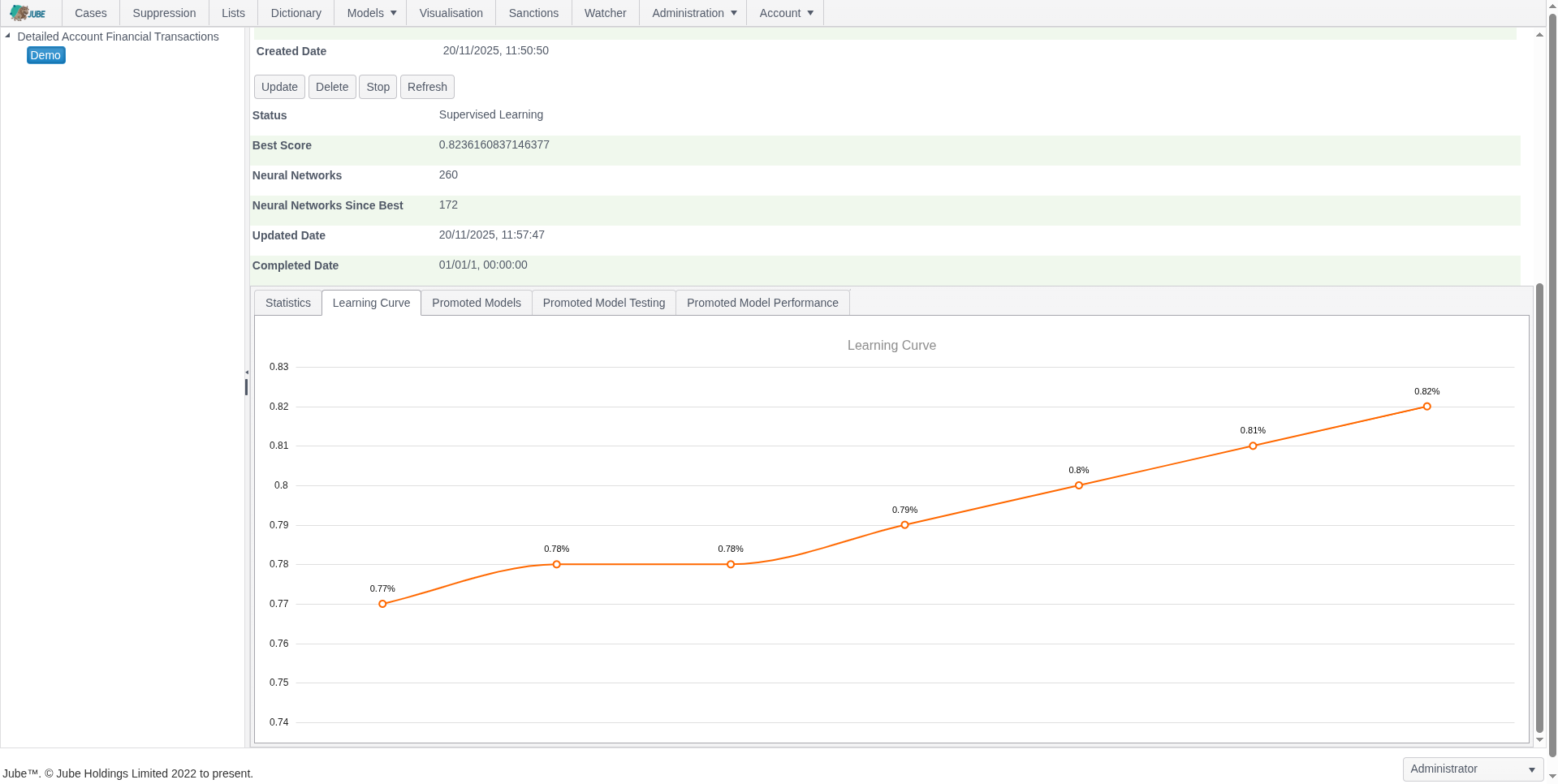
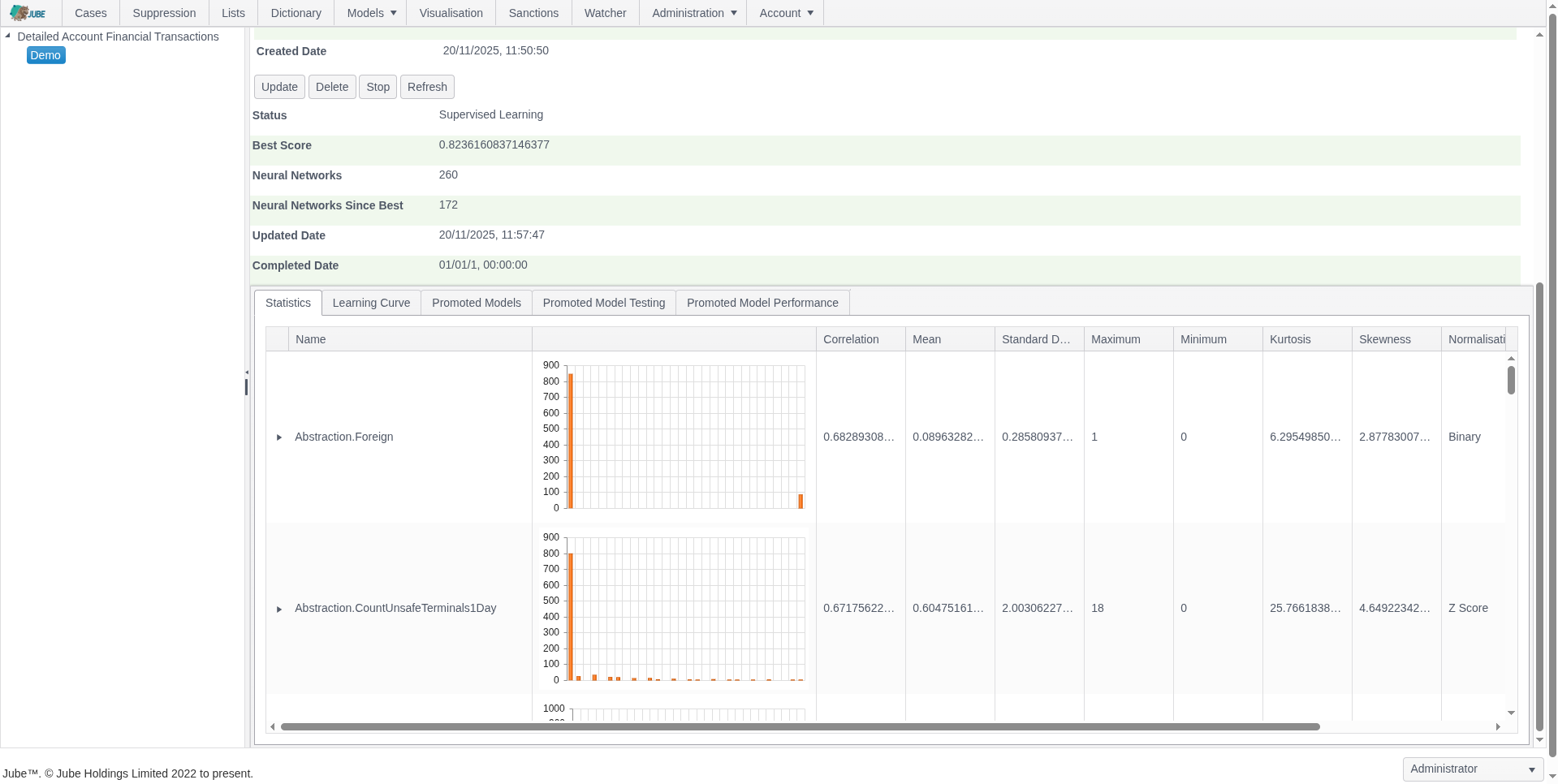
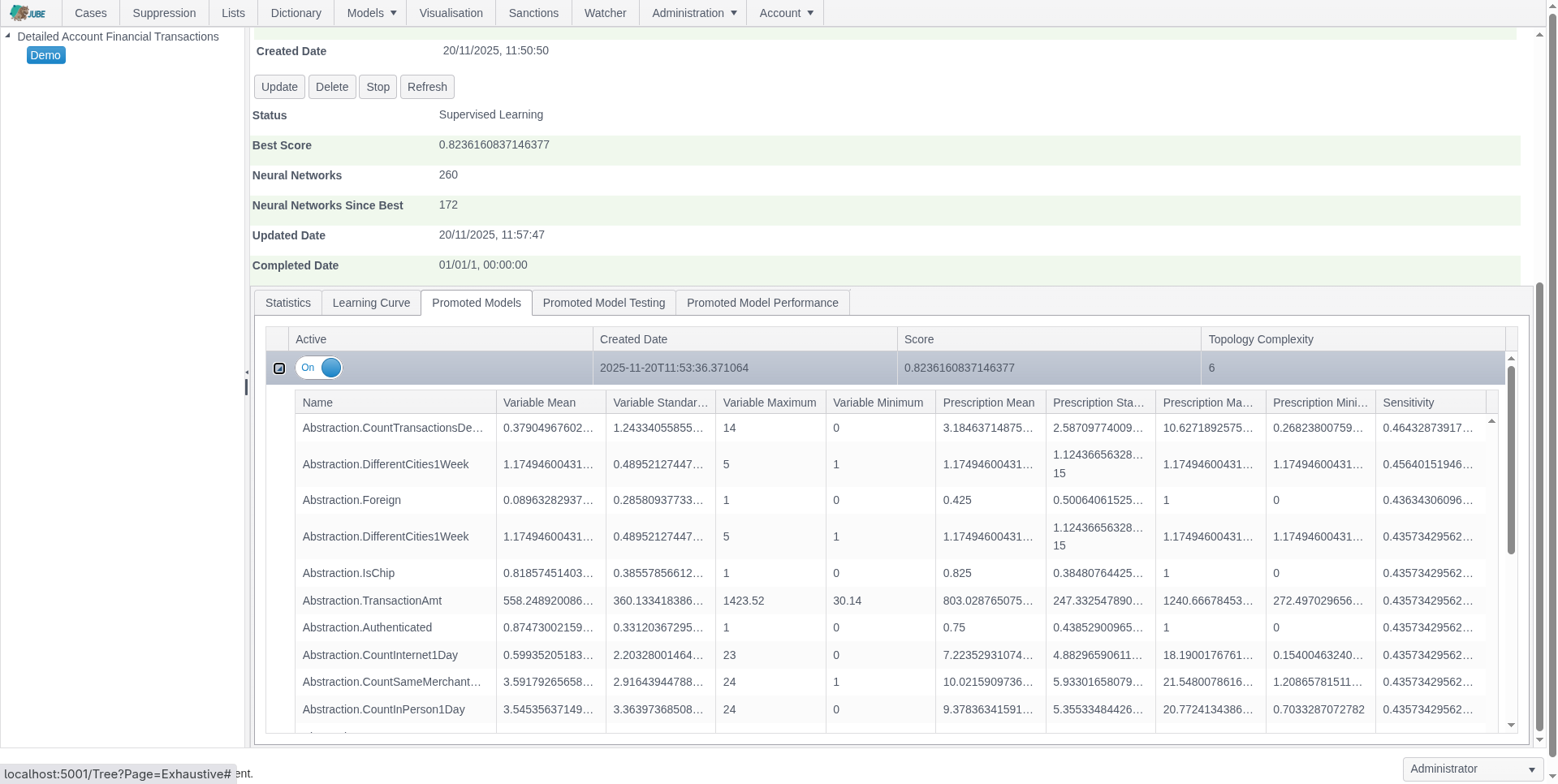
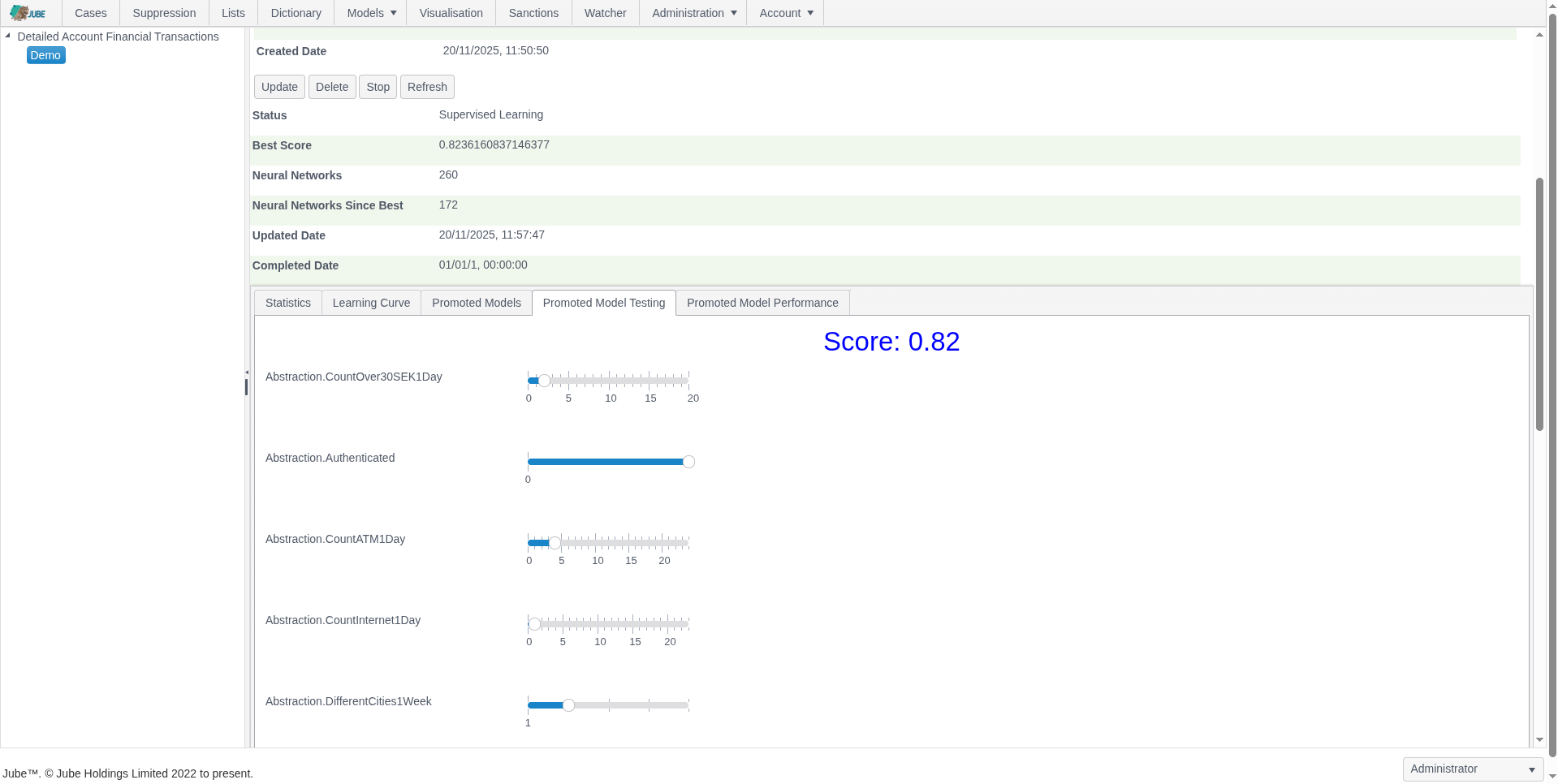
Adaptive Machine Learning — Exhaustive Adaptation
Jube leverages adaptive machine learning for AML and fraud detection, combining anomaly detection, supervised risk models, and continuous model training to identify both known and emerging threats, while deriving behavioral features for interpretable and actionable risk insights.
- Unsupervised learning identifies deviations from normal customer behavior for anomaly detection
- Supervised learning models detect known fraud and AML patterns based on historical data
- A hybrid approach combines supervised and unsupervised methods
- “Exhaustive Adaptation” evolves the model topology — trying different neural-network structures and variables — to find well‑generalized, computationally efficient models as data patterns change
- Behavioral feature abstraction derives signals such as transaction volume, velocity, and geolocation to improve ML model interpretability
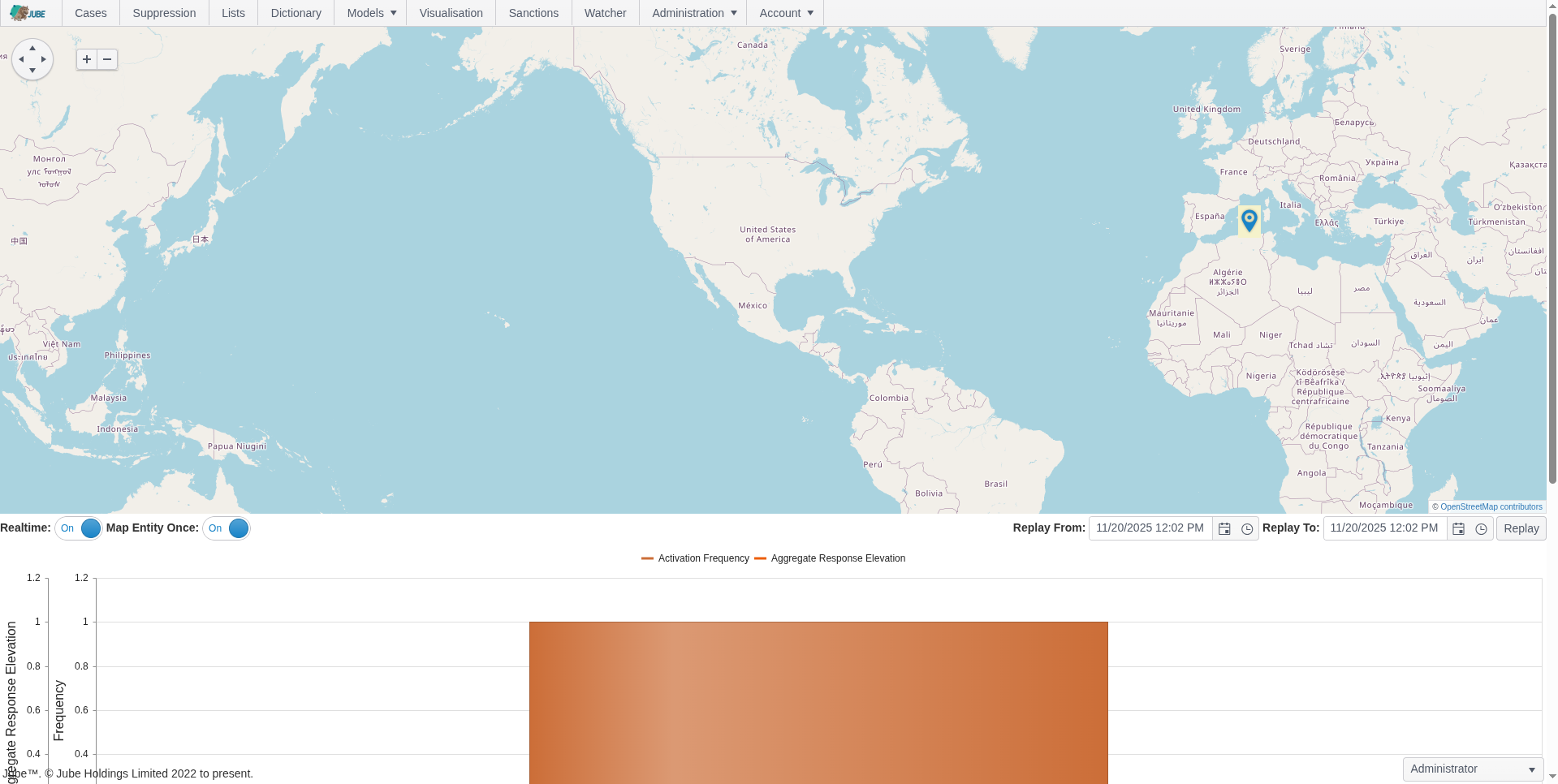
Real-Time Transaction Monitoring
Jube’s real-time transaction monitoring engine detects suspicious activity instantly, enabling financial institutions and fintechs to respond to fraud and AML risks as they occur. The engine combines low-latency processing, scalable architecture, and reliable storage to handle large transaction volumes efficiently.
- Stateless, horizontally scalable architecture
- Low-latency, in-memory processing with Redis for real-time state mutable state
- Frequently accessed immutable state stored locally also to minimize network overhead, reduce serialization/deserialization, and increase server density, ensuring fast, scalable decisioning under high load
- Durable storage and audit logs with PostgreSQL
- AMQP integration (RabbitMQ) for inbound and outbound events
- Full support for synchronous and asynchronous interfaces via HTTP, AMQP, and hybrid modes
- Asynchronous archival of decision payloads for analytics and reporting
- Real-time reprocessing of past data available for integration of fresh intelligence and analysis of exposure
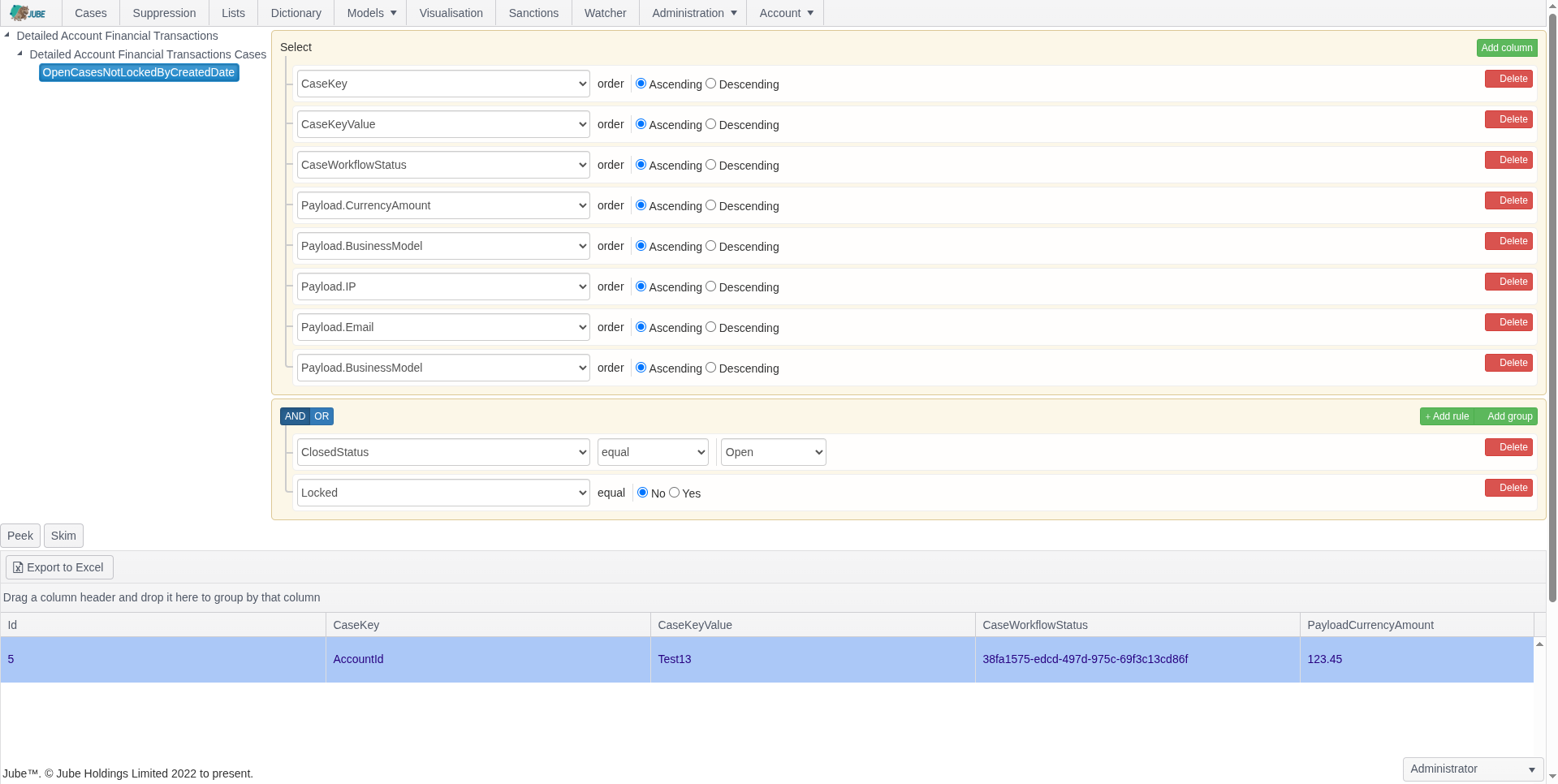
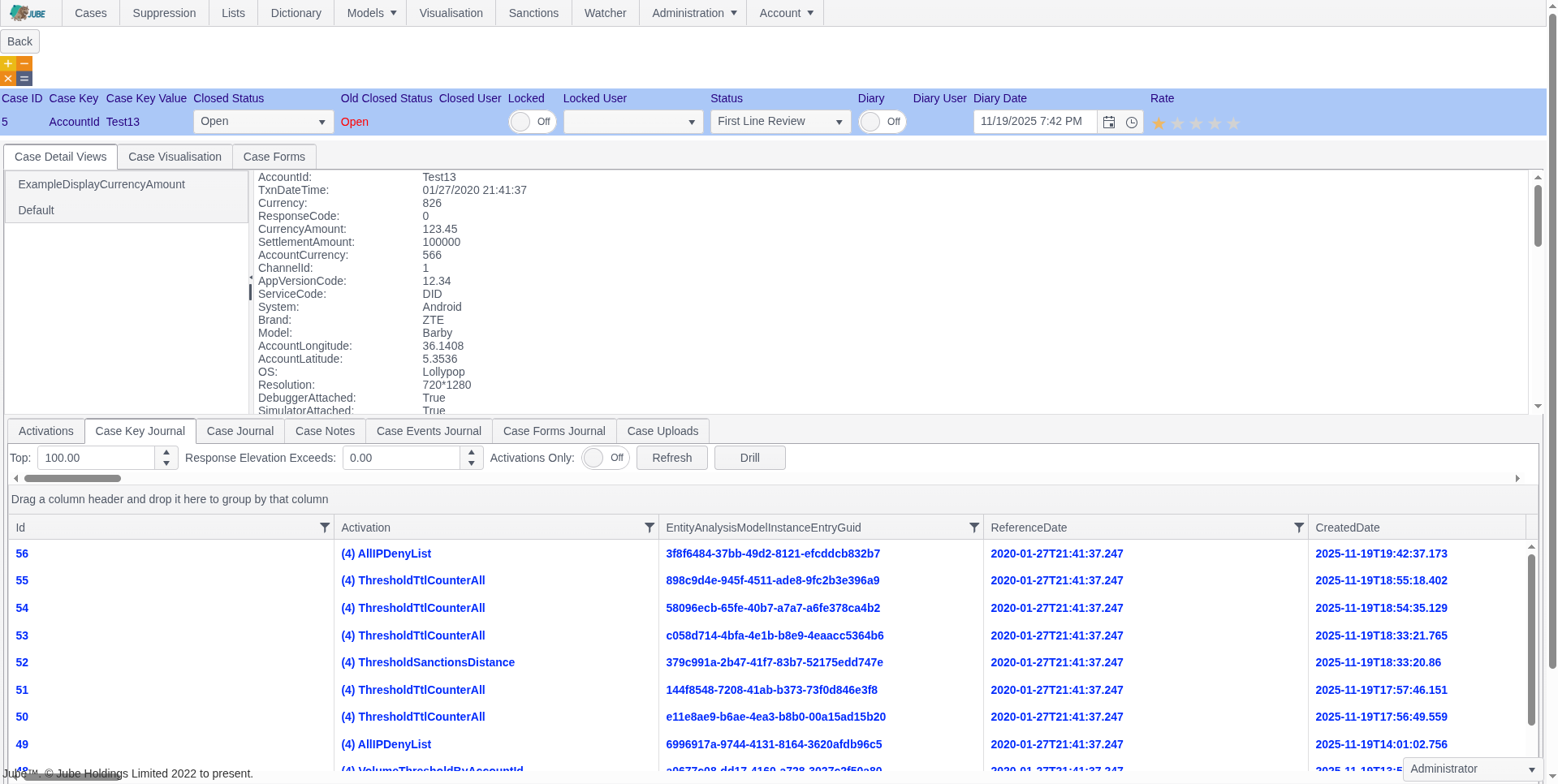
Case Management for Compliance
Jube delivers workflow-driven AML and fraud case management with automated escalation, full audit trails, and document versioning, giving compliance teams an end-to-end solution for investigating suspicious transactions efficiently.
- Multiple case streams (AML, fraud, compliance)
- Workflow-driven dashboards for investigators
- Document upload and versioning (EDD, CDD, ID verification)
- Automatic case escalation via activation rules
- Full audit trails for all actions
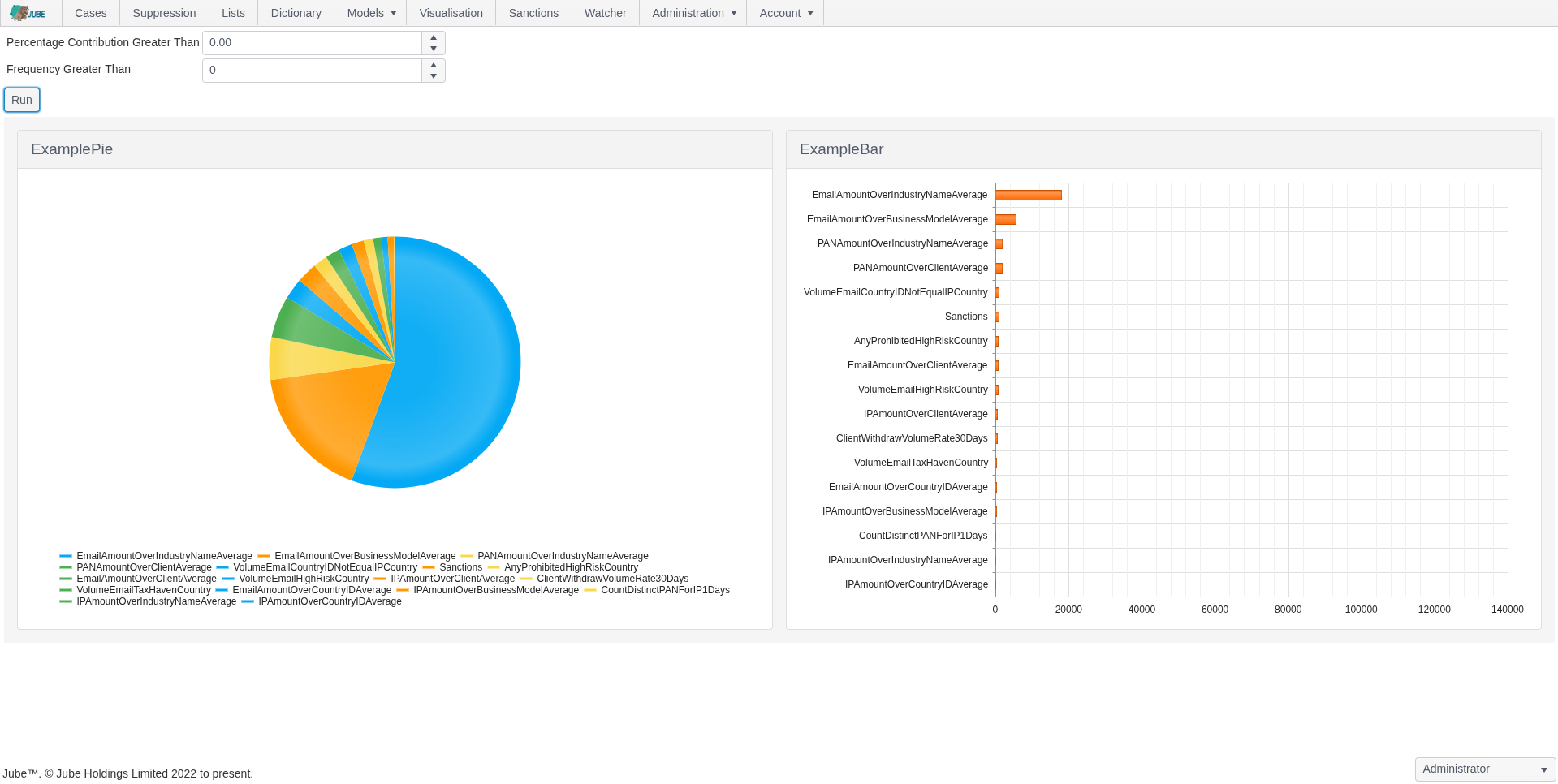
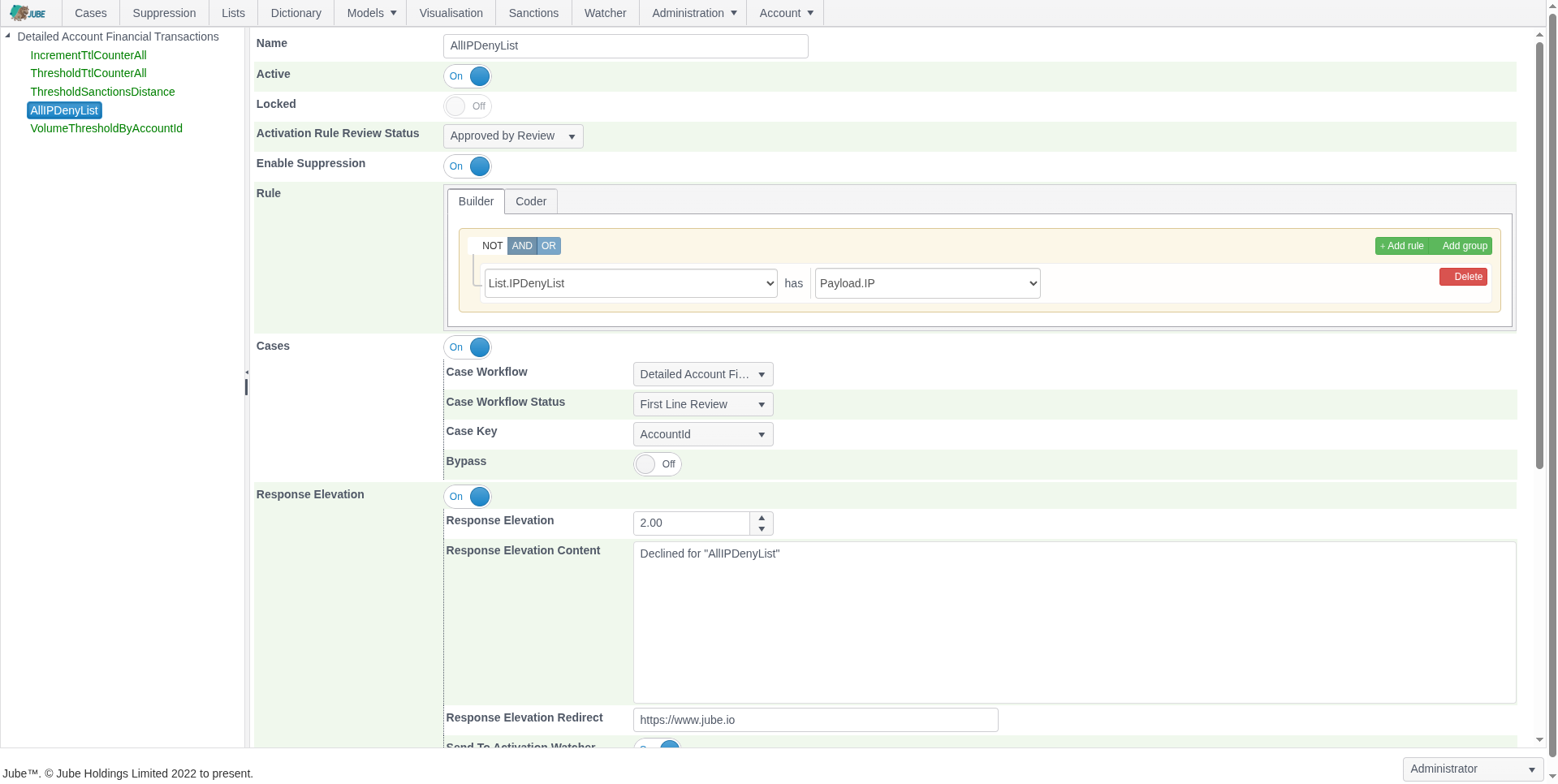
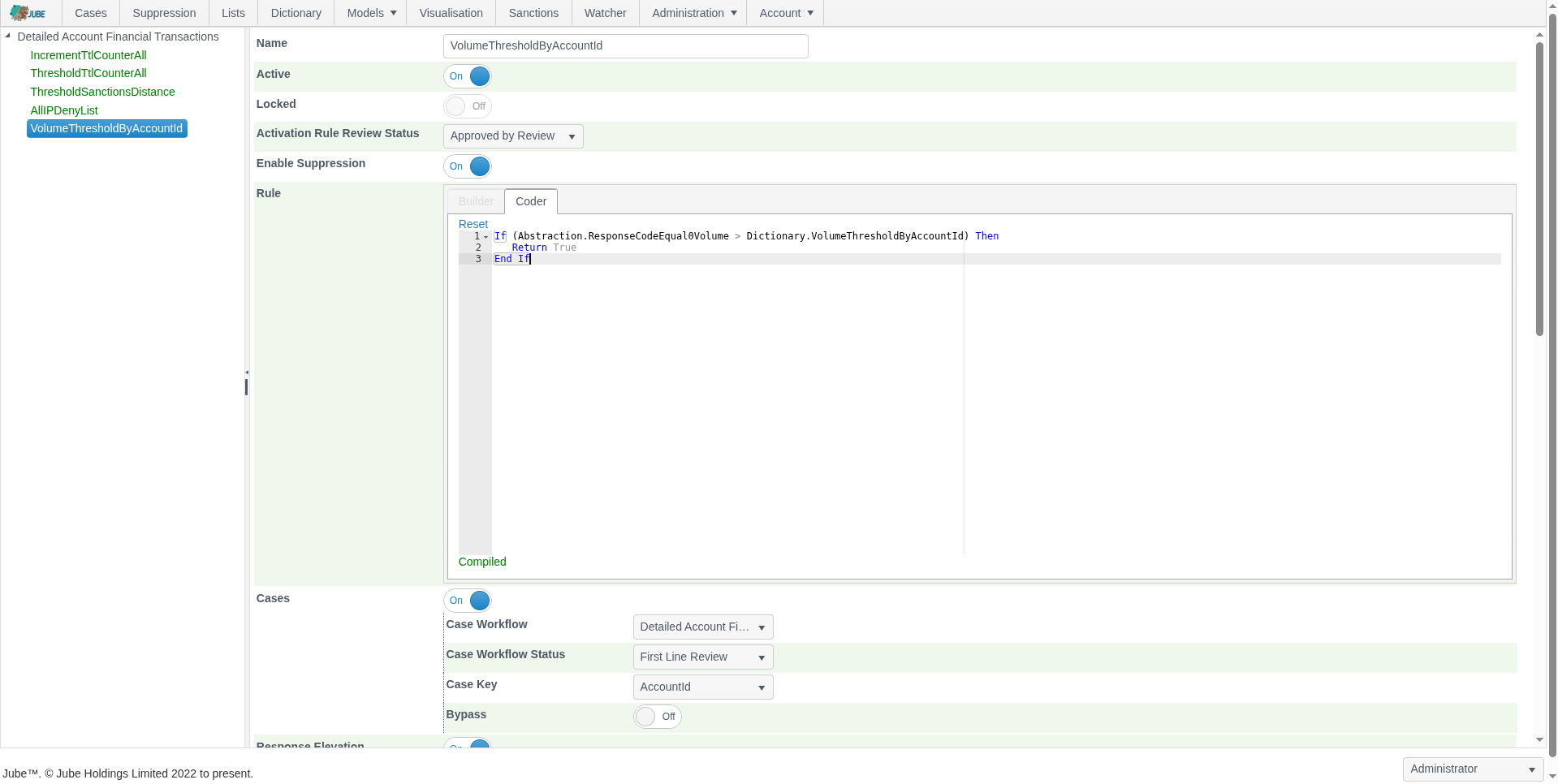
Flexible Rule Engine
Jube’s rules engine supports thresholds, velocity checks, aggregation counts, and sanctions screening, fully integrated with ML outputs for comprehensive detection.
- Threshold-based detection
- Velocity and aggregation checks
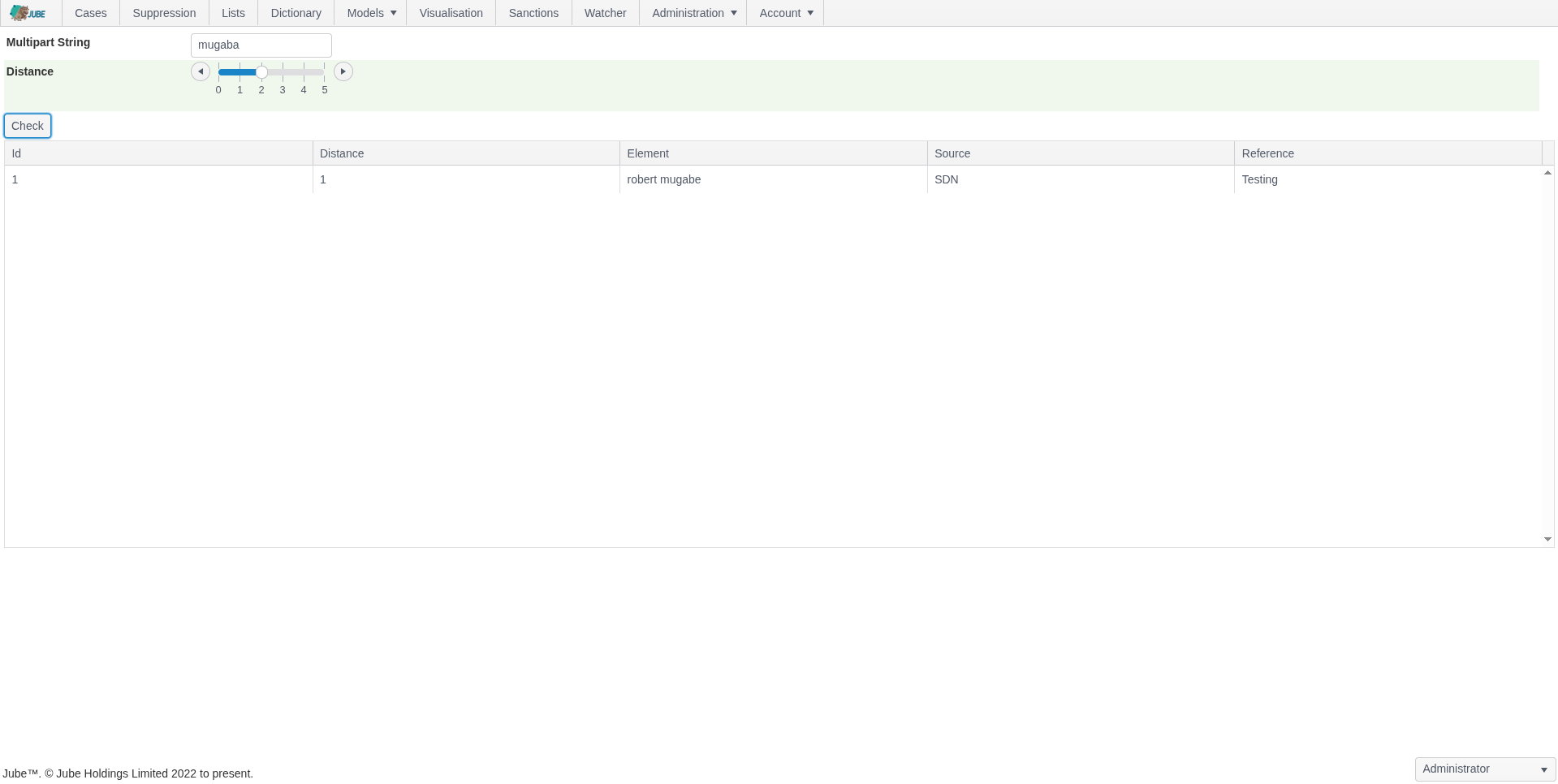
- Automatically check transactions and counterparties against global sanctions lists for regulatory compliance
- Time-to-live counters and suppression
- Fully integrates with ML outputs for combined detection
- Online or background preparation of velocity and other aggregations depending on data volume
Cloud-Native
Jube’s architecture is purpose-built for open source fraud detection and AML transaction monitoring. It’s fully containerized (Docker, Kubernetes), supports multi-tenancy, and is highly scalable — making it a top-tier AML and fraud detection software open source solution.
The platform preserves configuration, enabling institutions to back up, restore, and migrate rules, workflows, and ML settings. This ensures operational continuity and smooth system upgrades or deployments.
Jube supports multi-tenancy, allowing financial institutions or service providers to monitor transactions for multiple sub-clients (brands or business units) within a single deployment. Each tenant can maintain independent rules, workflows, and ML configurations.
See Jube open source AML software and open source fraud detection software in action:
